

“Let’s make the most out of INSPIRE!” – That was the title of the data challenge hosted at this year’s Inspire Helsinki event.
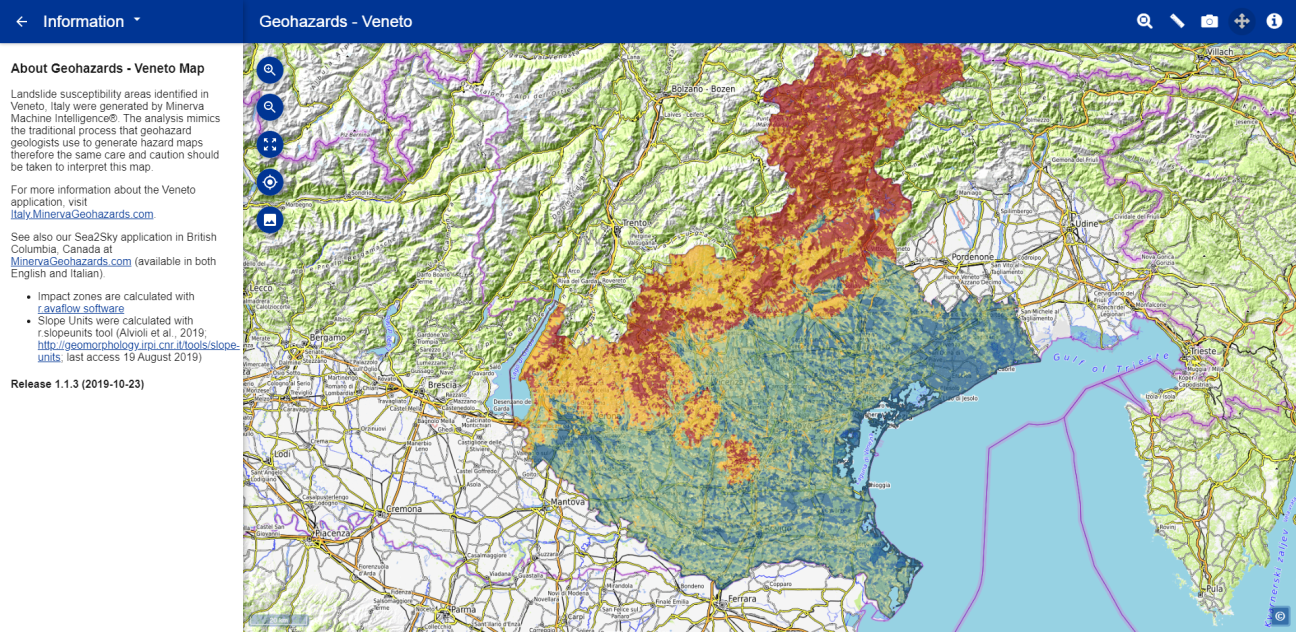
Minerva Intelligence, a Canadian based company with a recently opened subsidiary office in the EU, took that challenge up, and won the overall competition. Their challenge submission showed Landslide Susceptibility for different landslide types in the Veneto Region of Italy.
Jake McGregor, Section Head of Geospatial Technology at the Minerva team, said: “This was indeed quite the challenge! We had to learn about the INSPIRE code lists and data structures, as well as try to find Italian INSPIRE data covering our study area, but in the end we found workable solutions for all problems and were able to provide an end-to-end solution built on INSPIRE components such as the Data Specifications toolkit and the Re3gistry”.
To overcome data gaps they aligned critical input layers from Italian data sources to INSPIRE data structures and terminology using hale studio, and hosted INSPIRE view and download services on hale connect.
Moreover, in order to distinguish between different landslide types, Minerva needed to extend the INSPIRE Natural Hazard Category code list. Minerva’s Natural Hazard classification extension is based on the seminal 2014 landslide classification paper by Hungr et al., “The Varnes classification of landslide types, an update”. The code list hierarchy was structured in Minerva’s open-access taxonomy creation tool, ACE. For the data challenge Minerva also created a schema extension to INSPIRE’s Natural Risk Zones theme to include “susceptibility area” as a unique ‘feature type’.
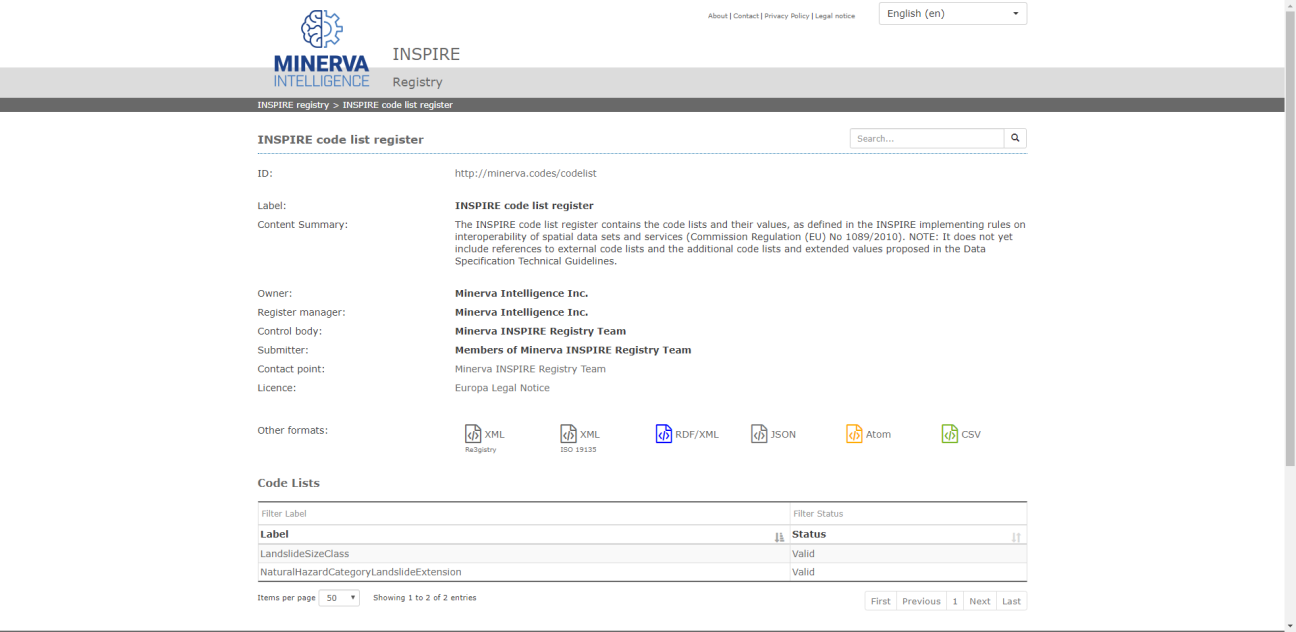
To share the code list terms and the feature type, with support from the JRC, Minerva configured and hosted an instance of the Re3gistry software. The Re3gistry is an open source solution for managing and sharing reference codes developed by the JRC, currently managed through the ELISE Action. So far it has been successfully implemented by 10 users across several countries.
“The Re3gistry allowed us to formally register the concepts we needed for our application to work and it makes that knowledge structure publicly available for re-use and interoperability.” -said Jake McGregor.
Currently, Minerva's registry contains one code list extension, one original code list and two feature types. Minerva plans to host more INSPIRE extensions related to the geologic and environmental domains they are working in.
This work is an example of semantic data interoperability being implemented by the private sector, making use of tools created by the European Commission and adding value to INSPIRE compliant datasets. Minerva’s work shows the real-world value of INSPIRE implementation.